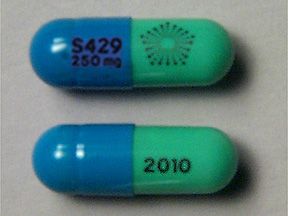
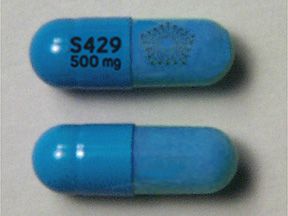
Pentasa (mesalamine) is a brand-name prescription medication. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved it to treat ulcerative colitis in certain adults.
Pentasa comes as a capsule that you swallow. It belongs to a drug class called aminosalicylates.
Currently, Pentasa is only available in a brand-name form. There are currently no generic forms of Pentasa available. However, mesalamine, the active ingredient in Pentasa, is available as generic extended-release tablets in other strengths.
For information about the dosage of Pentasa, including its strengths and how to take the drug, keep reading. For a comprehensive look at Pentasa, see this article.
This article describes typical dosages for Pentasa provided by the drug’s manufacturer. When taking Pentasa, always follow the dosage prescribed by your doctor.
Your doctor will recommend the best dosage of Pentasa for you.
Pentasa form
Pentasa comes as an oral capsule.
Pentasa strengths (250 mg and 500 mg)
Pentasa comes in two strengths: 250 milligrams (mg) and 500 mg.
Typical dosages
Typically, your doctor will prescribe the smallest dosage of Pentasa that provides the desired effect.
The following information describes dosages that are commonly used or recommended. However, be sure to take the dosage your doctor prescribes for you. Your doctor will determine the best dosage to fit your needs.
Dosage for ulcerative colitis
The recommended dosage of Pentasa for ulcerative colitis is 1,000 mg taken four times per day. The total daily dosage is 4,000 mg per day. Each dose can be taken as four 250 mg capsules or two 500 mg capsules.
Long-term treatment
Pentasa is meant to be a long-term treatment. If you and your doctor determine that Pentasa is safe and effective for you, you’ll likely take it long term.
Below are the answers to some frequently asked questions about Pentasa.
What’s Pentasa’s dosage for Crohn’s disease?
Pentasa is not approved to treat Crohn’s disease. At this time, Pentasa is only approved to treat certain types of ulcerative colitis. Because of this, there isn’t a recommended dosage of Pentasa for Crohn’s disease.
However, it’s possible that your doctor may prescribe Pentasa off-label to treat your Crohn’s disease. Using a drug off-label is when your doctor prescribes a medication for a different use than what it was approved for. In this case, your doctor will be able to recommend the best dose of Pentasa for you.
What’s the dosage for the enema form of Pentasa?
Pentasa doesn’t come in an enema form at this time. It only comes as a capsule that you swallow.
However, the active ingredient in Pentasa, mesalamine, does come in the form of an enema. The brand name form of the mesalamine enema is called Rowasa (or sfRowasa, which is the sulfite-free form of the drug).
If you have questions about which form of mesalamine may be the best treatment option for you, talk with your doctor or pharmacist.
Pentasa comes as a capsule that you swallow four times per day. The amount of capsules you’ll take will vary depending on the strength of the capsule you are taking. Your capsules may be swallowed whole. You should drink plenty of water when you take your dose of Pentasa.
If you’re having trouble swallowing the Pentasa capsules, you can split open the capsules and sprinkle the entire contents onto applesauce or yogurt. If you do this, be sure to take your dose right away. Do not crush or chew the capsule or its contents.
You should try to take your dose of Pentasa about once every 6 hours. This helps maintain a steady level of the drug in your body so Pentasa can work effectively.
ACCESSIBLE DRUG LABELS AND CONTAINERSIf you’re having trouble reading your prescription label, talk with your doctor or pharmacist. Some pharmacies offer labels with large print, braille, or a code you scan with a smartphone to convert text to speech. If your local pharmacy doesn’t have these options, your doctor or pharmacist might be able to recommend a pharmacy that does.
If you’re having trouble opening medication bottles, ask your pharmacist about putting Pentasa in an easy-open container. They also may recommend tools that can make it easier to open bottles.
If you miss your dose of Pentasa, call your doctor or pharmacist. They can help you determine when to take your next dose of medication. In some cases, they may recommend taking a dose as soon as you remember. However, other times, your doctor or pharmacist may recommend skipping your missed dose and taking your next dose on your regular schedule.
To help make sure that you don’t miss a dose, try using a medication reminder. This can include setting an alarm or using a timer. You could also download a reminder app on your phone.
If you take more Pentasa than your doctor prescribes, you may develop serious side effects.
It’s important that you do not take more Pentasa than your doctor advises.
Symptoms of an overdose
Overdose symptoms of Pentasa can include:
- nausea or vomiting
- abdominal pain
- headache
- dizziness
- confusion
- seizures
- rapid or deep breathing
- ringing in your ears
- liver or kidney damage
If you take more than the recommended amount of Pentasa
Call your doctor right away if you believe you’ve taken too much Pentasa. Another option is to call the American Association of Poison Control Centers at 800-222-1222 or use its online tool. If you have severe symptoms, immediately call 911 or your local emergency number, or go to the nearest emergency room.
The dosages in this article are typical dosages provided by the drug manufacturer. If your doctor recommends Pentasa for you, they will prescribe the dosage that’s right for you. Always follow the dosage that your doctor prescribes for you.
As with any drug, never change your dosage of Pentasa without your doctor’s recommendation. If you have questions about the dosage of Pentasa that’s best for you, talk with your doctor.
Besides learning about dosage, you may want other information about Pentasa. These additional articles might be helpful to you:
- More about Pentasa. For information about other aspects of Pentasa, refer to this article.
- Side effects. To learn about side effects of Pentasa, see this article. You can also look at the Pentasa prescribing information.
- Details about ulcerative colitis. For details about ulcerative colitis, see our inflammatory bowel disease hub.
Disclaimer: Medical News Today has made every effort to make certain that all information is factually correct, comprehensive, and up to date. However, this article should not be used as a substitute for the knowledge and expertise of a licensed healthcare professional. You should always consult your doctor or another healthcare professional before taking any medication. The drug information contained herein is subject to change and is not intended to cover all possible uses, directions, precautions, warnings, drug interactions, allergic reactions, or adverse effects. The absence of warnings or other information for a given drug does not indicate that the drug or drug combination is safe, effective, or appropriate for all patients or all specific uses.