Ground glass opacity (GGO) refers to the hazy gray areas that can show up in CT scans of the lungs. These areas show increased density inside the lungs which could indicate pneumonia or other respiratory disorders.
The term comes from a technique in glassmaking during which the surface of the glass is blasted by sand. This technique gives the glass a hazy white or frosted appearance.
This article will look at what GGO is, some of its causes, and its treatment options.
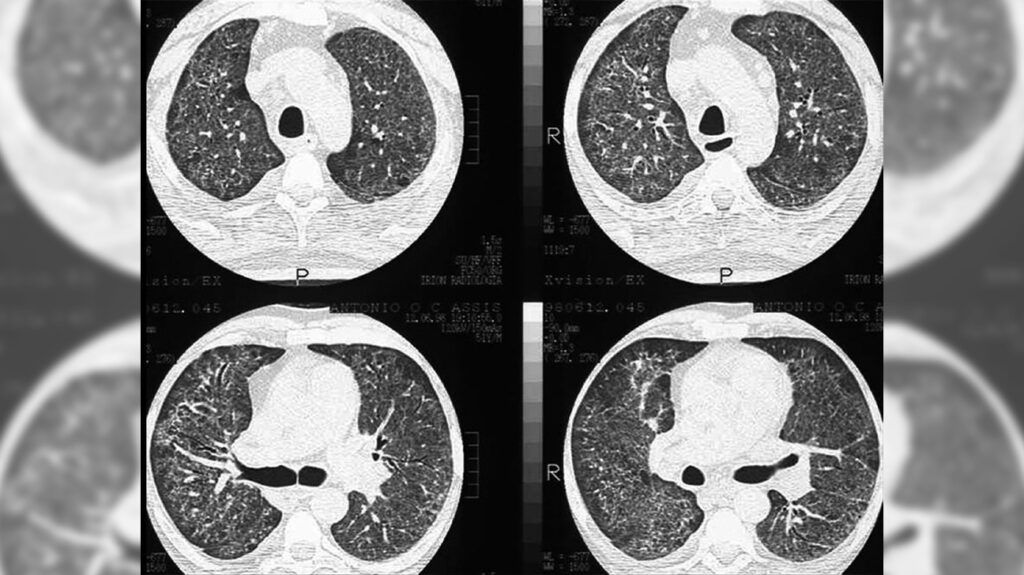
GGO refers to gray areas that can show up in lung CT scans.
Normally, the lungs appear black in X-ray and CT scans. This indicates that they are free of any visible blockages.
However, gray areas indicate increased density, meaning that something is partially filling the air spaces inside the lungs. This could be due to:
- the air spaces becoming partially filled with fluid, pus, or cells
- the walls of the alveoli, which are the tiny air sacs in the lungs, thickening
- the space between the lungs thickening
GGO can be due to many conditions. Sometimes, the cause is benign. Other times, it may be the temporary result of a short-term illness. However, it can also indicate a more serious or long-term condition.
There are several types of GGO. These include:
- Diffuse: Diffuse opacities show up in multiple lobes of one or both lungs. This pattern occurs when the air in the lungs is replaced with fluid, inflammation, or damaged tissue.
- Nodular: This type can indicate both benign and malignant conditions. GGO that persists over several scans may indicate either premalignant or malignant growths.
- Centrilobular: This type appears within one or several lobules of the lung. Lobules are the hexagonal divisions of the lung. The connective tissue between the lobules is unaffected.
- Mosaic: This pattern develops when small arteries or airways within the lung are blocked. The opaque areas vary in intensity.
- Crazy paving: Crazy paving shows up as a linear pattern. It can occur when the spaces between the lobules widen.
- Halo sign: This type of opacity fills the area around the nodules.
- Reversed halo sign: A reversed halo sign is an area that is almost totally surrounded by liquid-filled tissue.
The shape, size, quantity, and location of opacities will vary depending on the cause. Some conditions cause only one type, but others may cause a mixture.
The sections below will look at some potential causes in more detail.
Infections are common causes of GGO. Such infections include:
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is a serious infection in the lungs. It can result from viruses, bacteria, or fungi.
The symptoms can vary depending on the cause, but they typically include:
- a cough that produces yellow, green, or bloody mucus
- blue or white lips and fingernails
- shortness of breath
- fever and sweating
- extreme fatigue
- confusion or delirium
- a sharp pain in the chest that gets worse when coughing or breathing deeply
- loss of appetite
A doctor may prescribe antiviral medications to treat viral pneumonia. Doctors also treat bacterial and fungal pneumonia with medications. However, sometimes symptom management and rest is enough.
COVID-19
A 2020 systematic review and meta-analysis found that just over
Another
The symptoms of COVID-19 can include
- fever
- chills
- a cough
- shortness of breath
- new loss of smell or taste
- fatigue
- muscle aches
- headache
- sore throat
- runny or congested nose
- nausea and vomiting
- diarrhea
Learn more about COVID-19 symptoms and what to do if they occur here.
Pneumonitis, or inflammation in the lungs, can occur if a person inhales:
- allergens or irritants, which can contribute to hypersensitivity pneumonitis
- electronic cigarette smoke, which can cause e-cigarette or vaping product use-associated lung injury (EVALI)
- toxins, such as asbestos
Certain drugs can also cause pneumonitis and accompanying GGO. Typically, this type of pneumonitis occurs shortly after a person begins taking a new drug.
Hypersensitivity pneumonitis
The symptoms of hypersensitivity pneumonitis can include:
- a cough
- short-term shortness of breath
- fever
- pain
Other names for this condition include farmer’s lung and hot tub lung.
In the short term, doctors treat this condition by trying to identify and remove the trigger of a person’s symptoms. The person may also require medications and oxygen therapy.
In the long term, the condition may cause chronic fatigue, weight loss, and irreversible scarring.
EVALI
E-cigarettes and vaping devices contain nicotine concentrates, solvents, and other chemicals. These products can cause EVALI.
EVALI may cause
Vaping can also cause alveolar hemorrhage. There is more detail on this condition below.
Interstitial lung disease is an umbrella term that includes many different conditions. They all cause inflammation and scarring around the alveoli, lining of the lungs, and blood vessels.
These conditions could be due to an autoimmune disease, a connective tissue disorder, or toxin exposure.
The progression of interstitial lung disease varies from person to person depending on what caused it.
Symptoms vary from mild to severe. They may include:
- shortness of breath
- labored breathing
- a dry cough
- severe tiredness or weakness
- mild chest pain
- unexplained weight loss
Treatment aims to slow the progression of the condition. Doctors may use supplemental oxygen, anti-inflammatory drugs, or immunosuppressant drugs.
Pulmonary edema is the result of fluid collecting in the air spaces of the lungs. It can be due to several conditions, including heart failure and altitude sickness.
Symptoms include:
- coughing up blood
- shortness of breath
- difficulty breathing when lying down
- sweating
- restlessness
- blue- or white-tinged fingertips or lips
People with these symptoms should seek medical attention immediately, as sudden pulmonary edema can be an emergency.
Alveolar hemorrhage occurs when the blood vessels in the lungs become damaged, leading to bleeding.
It is a medical emergency that can result from numerous conditions, including autoimmune diseases, vasculitis, and bleeding disorders.
The symptoms can vary widely and may include:
- coughing up blood
- difficulty breathing
- anemia
- respiratory failure
Doctors treat most cases of alveolar hemorrhage with steroids to reduce inflammation and immunosuppressants to stop the immune system from damaging the blood vessels further.
Sometimes, GGO nodules in the lung can indicate cancer.
Lung cancer may not have pronounced symptoms in the early stages of the condition. However, a person should speak with their doctor if they experience:
- a persistent cough that worsens
- shortness of breath
- pain in the chest, shoulders, or back
- voice changes
- weight loss
Treatment varies according to the severity and type of cancer a person has. It may include chemotherapy, surgery, and radiation therapy.
After a doctor finds GGO in a CT scan, they will take note of the size, shape, location, and distribution of the opacities to determine the likely cause.
They may also order more tests, such as:
- lung function tests
- sputum tests
- blood tests
- bronchoscopy
- lung biopsy
- a CT scan, for those who have received X-rays, as CT scans show more detail
They may also order electrocardiography and echocardiography to see if a person’s lung problems could be the result of a heart condition.
Receiving test results can be worrying. Here are some questions that a person may wish to ask their doctor:
- What can the scan results tell us?
- In which part of the lung is the GGO?
- What type of GGO is present? Are there multiple types?
- Could it indicate a benign condition?
- Will other diagnostic tests help determine the cause?
The following are commonly asked questions about GGO.
How serious is GGO?
GGO develops due to many conditions, meaning that there are varying degrees of severity. Some causes are benign, and other causes can be more serious, such as lung cancer.
Is GGO a tumor?
GGO nodules are an important indicator of lung cancer. However, it is important to remember that there are many causes of GGO, which can be present in benign conditions.
GGO can show up on a CT scan of the lungs. It appears as hazy gray areas that can indicate a range of conditions.
Some causes of GGO may be benign and resolve on their own, while others may be chronic.
