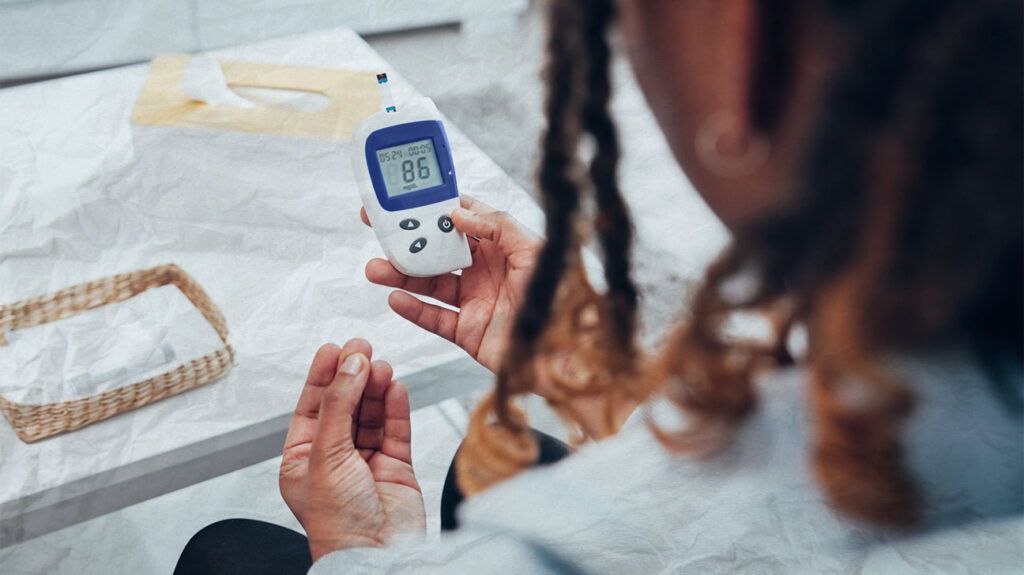
Hypoglycemia is the term for low levels of sugar in the blood. Refractory hypoglycemia occurs when hypoglycemia lasts for a prolonged period of time, such as a few hours to a few days.
Refractory hypoglycemia can occur when a person takes high doses of long-lasting insulin. It may also occur due to certain tumors that release proteins that can affect a person’s blood sugar levels.
A person can usually treat regular hypoglycemia on their own by consuming foods containing sugar or carbohydrates. However, refractory hypoglycemia may require treatment with intravenous glucose to help increase blood sugar levels.
This article explains what refractory hypoglycemia is and what can cause it. It also looks at risk factors and treatments for the condition.
Currently, there
- lasts for hours or days
- requires a high dose of dextrose to normalize sugar levels
- requires a prolonged infusion of glucose to normalize sugar levels
A person with refractory hypoglycemia may experience the
- fast heartbeat
- shaking
- sweating
- nervousness or anxiety
- irritability
- confusion
- dizziness
- hunger
Severe symptoms of refractory hypoglycemia include seizures and coma.
Generally, a person can treat hypoglycemia quickly and easily by consuming foods containing sugars. Their blood sugar may return to a normal range
However, with refractory hypoglycemia, the condition lasts longer. Evidence suggests that refractory hypoglycemia can last anywhere from
Taking
Insulin is a hormone that regulates blood sugar. People with diabetes may take insulin to
If a person takes a very high dose of long-lasting insulin, it can cause their blood sugar levels to drop for a long period of time. This can lead to refractory hypoglycemia.
Read on to learn more about insulin therapy.
Certain tumors
NICH is a rare condition that occurs when a tumor secretes a protein called insulin-like growth factor-2 (IGF-2). This protein can lower a person’s blood sugar levels, causing them to develop refractory hypoglycemia.
One cause of refractory hypoglycemia is a
NICH
Mesenchymal tumors are tumors
Epithelial tumors are types of tumors
NICH is most often associated with hepatocellular carcinoma,
A person can usually treat hypoglycemia by eating or drinking
Learn more about the rule of 15 for treating hypoglycemia.
However, if a person has refractory hypoglycemia, their symptoms may not respond to this standard treatment.
Treatment for refractory hypoglycemia
Dextrose is a type of sugar that medical professionals
In some cases, a medical professional will then administer a prolonged IV infusion of glucose. This ensures a person’s blood sugar levels remain within their target range after they receive dextrose.
Refractory hypoglycemia occurs when a person experiences hypoglycemia that lasts for a prolonged period of time.
There is no universal definition of refractory hypoglycemia. Medical professionals often define it as hypoglycemia that lasts for hours or days. It may also require high doses or prolonged infusions of glucose to normalize sugar levels.
Refractory hypoglycemia can occur when a person takes very high doses of long-lasting insulin. It may also occur due to certain tumors that release proteins that can affect blood sugar levels.
If a person has refractory hypoglycemia, they may require treatment with glucose to help increase their blood sugar levels.
