Painful ejaculation can happen as a result of prostate disorders, medication, sexually transmitted infections (STIs), and more. In some cases, pain may feel like a burning sensation.
Some men feel embarrassed when ejaculation is painful, but it is a relatively common symptom. It is also highly treatable and can be the first symptom of another problem, such as swelling in the prostate.
In this article, we examine the symptoms and causes of painful ejaculation, along with what can be done to treat them.

Pain may occur during or following ejaculation and may be located in the penis, bladder, or rectum.
The symptoms of painful ejaculation vary from man to man. They may also change over time.
Some men only experience symptoms after having sex with a partner, but not when they masturbate.
A few of the
- pain during or immediately following ejaculation
- pain in or around the penis, bladder, or rectum
- pain that begins shortly before or after ejaculation
- pain during urination, especially immediately after ejaculating
The pain may last only a few minutes, or for up to 24 hours following ejaculation. It can be mild or very intense.
For more research-backed information and resources for men’s health, please visit our dedicated hub.
A wide range of conditions can cause painful ejaculation.
In most men, pain during ejaculation is due to a medical condition. Sometimes, doctors are unable to find a medical cause. When this occurs, some men may need support in the form of psychotherapy to manage their condition.
Prostate disorders
Painful ejaculation may be linked to issues with the prostate.
Most of the medical literature on painful ejaculation focuses on problems with the prostate. Prostatitis is one common cause.
Men with prostatitis have swelling and inflammation of the prostate. This swelling is often due to a prostate infection. Prostatitis can also be caused by other issues, such as nerve damage or a urinary tract infection (UTI) that damages the prostate.
Men with diabetes are more likely to experience nerve damage that causes prostatitis.
A condition called benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), which causes the prostate to enlarge, may also affect ejaculation. Men with BPH may also experience painful or difficult urination or frequent urges to urinate.
Other prostate problems, including surgery on the prostate and prostate cancer, can also cause painful ejaculation.
Medication
Some medications can cause painful ejaculation. Antidepressants may cause a range of sexual issues, including changes in libido, erectile dysfunction (ED), and
Relationship and emotional problems
Depression, anxiety, and stress can radically change a man’s sex life. Likewise, problems in a relationship may manifest as physical symptoms, including painful ejaculation.
Men who experience no pain when they masturbate may have painful ejaculation because of emotional or relationship problems.
Seminal vesicle problems
The seminal vesicle is a gland where sperm mixes with other fluids to make semen. Problems with this gland, particularly hard growths called calculi, can make ejaculation painful.
Pelvic procedures
Procedures on the genitals or in the pelvis, including pelvic radiation, can damage the prostate and other parts of the body that play a role in ejaculation. This damage can make ejaculation painful.
Sexually transmitted infections
A wide range of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) can make ejaculation painful. Men may notice a burning sensation when ejaculating, urinating, or both. Chlamydia and trichomoniasis are common culprits.
Nervous system issues
Disorders that affect the nervous system, such as diabetes, can damage the nerves associated with orgasm and ejaculation.
Some physical injuries can also harm the nerves. Men with spinal cord injuries may experience a range of unusual sensations during ejaculation.
Mercury toxicity
Some case reports
Some people who experience painful ejaculation may also experience painful urination. When this happens, the cause may be one of these underlying problems:
- prostatitis
- BPH
- trichomoniasis
- chlamydia
Many nerves and tissues are involved in both ejaculation and urination. As a result, any conditions, injuries, or procedures that affect this area of the body could result in painful ejaculation and urination.
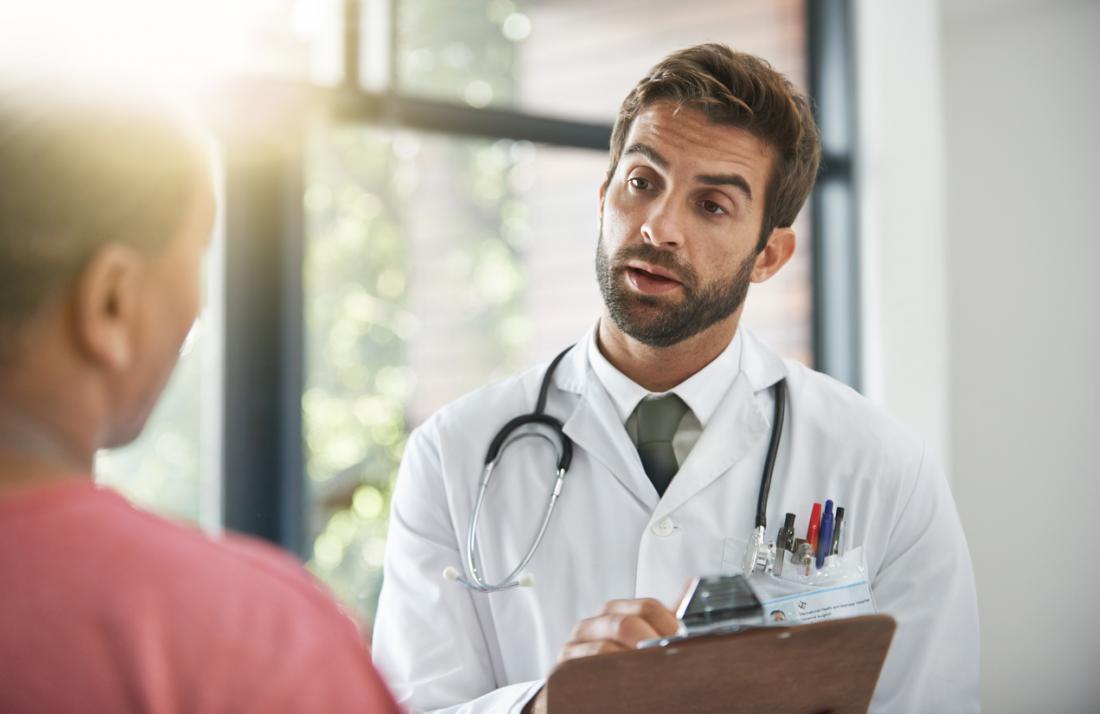

An examination may include questions about medications, relationships, and mental health.
Treatment for painful ejaculation depends on the cause.
An examination should begin with a complete medical history that includes questions about a man’s mental health and relationships. The doctor will ask about medications used currently and in the past, as well as any current or previous history of STIs. Comprehensive testing for STIs can also be helpful.
A pelvic exam, including a prostate exam, can assess for prostatitis, BPH, and injuries. The doctor may also perform blood work to test for prostate-specific antigen (PSA). This substance tends to rise in men with certain prostate conditions, including prostate cancer.
In most cases, treating the underlying cause also fixes symptoms of painful ejaculation. Some treatment options may include:
- antibiotics to treat a prostate infection or STI
- switching medications if the culprit is a drug
- surgery to treat prostate cancer and other prostate problems
- psychotherapy and lifestyle changes to address relationship and emotional problems
Nerve damage may be irreversible, but a doctor will probably still want to treat the underlying cause. Doing so can prevent nerve damage from getting worse.
When treatment fails, or a doctor cannot figure out the cause, a man can try some alternative strategies that may reduce the pain. Some options include:
- sex therapy
- pelvic floor exercises to strengthen the muscles involved in ejaculation
- pain medication
- muscle-relaxant medications
- anticonvulsant medications
Painful ejaculation is not dangerous, but it can undermine a man’s quality of life. Men who experience painful ejaculation may also report:
- loss of interest in sex
- shame
- relationship issues
- self-esteem issues
- fertility concerns
Though painful ejaculation itself is not dangerous, some of the conditions that cause it are. Lower quality of life should also be taken seriously and warrants medical treatment.
Men who experience painful ejaculation should see a doctor who specializes in genitourinary health or ejaculation dysfunction.
Early treatment can prevent underlying conditions from getting worse. In many cases, the cause is both easily treated and completely reversible.
Some men feel embarrassed about painful ejaculation, or uncomfortable discussing symptoms with their doctor. Others resign themselves to living with a less satisfying sex life. Men do not have to do this.
Painful ejaculation is a real medical problem that warrants prompt treatment.
A few discussions with a doctor may be all it takes to improve a man’s sex life and reduce his pain. There is no benefit to suffering in silence, especially since untreated painful ejaculation often gets worse.
