There are many different causes of ear drainage. The most common type of draining from the ear is earwax, which keeps the ear clean and healthy.
Other types of drainage and discharge include blood, clear fluid, and pus. These may signal a ruptured eardrum or ear infection.
Anyone who notices ear discharge after an injury to the head should seek medical attention straight away.
In this article, we look at the possible causes of ear drainage as well as treatment options and when to see a doctor.

Discharge from the ear can be a symptom of an infection.
Types and causes of ear drainage include:
Earwax
Earwax is normal drainage from the ear, and it can be white, yellow, or brown. The ears produce earwax to keep the ear clean and healthy and to protect it from infection.
If earwax mixes with water, for example, when someone bathes or swims, it can look like runny discharge.
Clear fluid
Clear fluid draining from the ear may be water, which can collect in the ear after swimming or bathing.
People can gently dry their ears after getting wet by holding a hair dryer on low heat away from their ear or by using a towel. Taking time to dry the ears can help prevent an infection called swimmer’s ear, in which water becomes trapped in the ear.
Doctors sometimes place an ear tube in the ears of people who get frequent ear infections. The ear tube provides an opening into the middle ear, which may allow a small amount of clear fluid to drain from the ear.
People should contact their doctor if any clear fluid drainage continues for more than 24 hours.
If a person notices clear fluid from their ears after an injury to the head, they should seek immediate medical attention.
Blood
A minor injury or scratch in the ear canal can sometimes cause a small amount of blood to exit the ear.
If a person has a ruptured eardrum, they may notice blood, pus, or clear fluid draining from the ear. The eardrum sits between the ear canal and the middle ear, and it can rupture if something creates a small hole in it.
The eardrum can rupture if:
- an ear infection puts pressure on the ear
- a loud noise happens very close to the ear
- a person inserts something too far into the ear
- someone experiences a sudden change in air pressure
- an injury occurs, such as a hit to the ear
A ruptured eardrum can cause the following symptoms:
- ear pain, then sudden relief
- ringing in the ear
- loss of hearing in the affected ear
If people notice any bleeding from the ear due to a head injury, they should seek immediate medical help.
Pus or cloudy fluid
Pus or cloudy fluid coming from the ear can be a sign of an ear infection in the ear canal or middle ear. The ear canal is the tube that joins the outer ear to the middle ear.
An infection of the middle ear, which doctors may refer to as otitis media, can cause fluid discharge from the ear. Ear infections can cause the eardrum to rupture in roughly 10 percent of cases. A ruptured eardrum can also cause drainage from the ear.
Ear infections can happen due to a cold, flu, or injury to the ear. Some people are more prone than others to frequent ear infections. If people have an ear infection, they may also have the following symptoms:
- an earache
- fever
- nausea
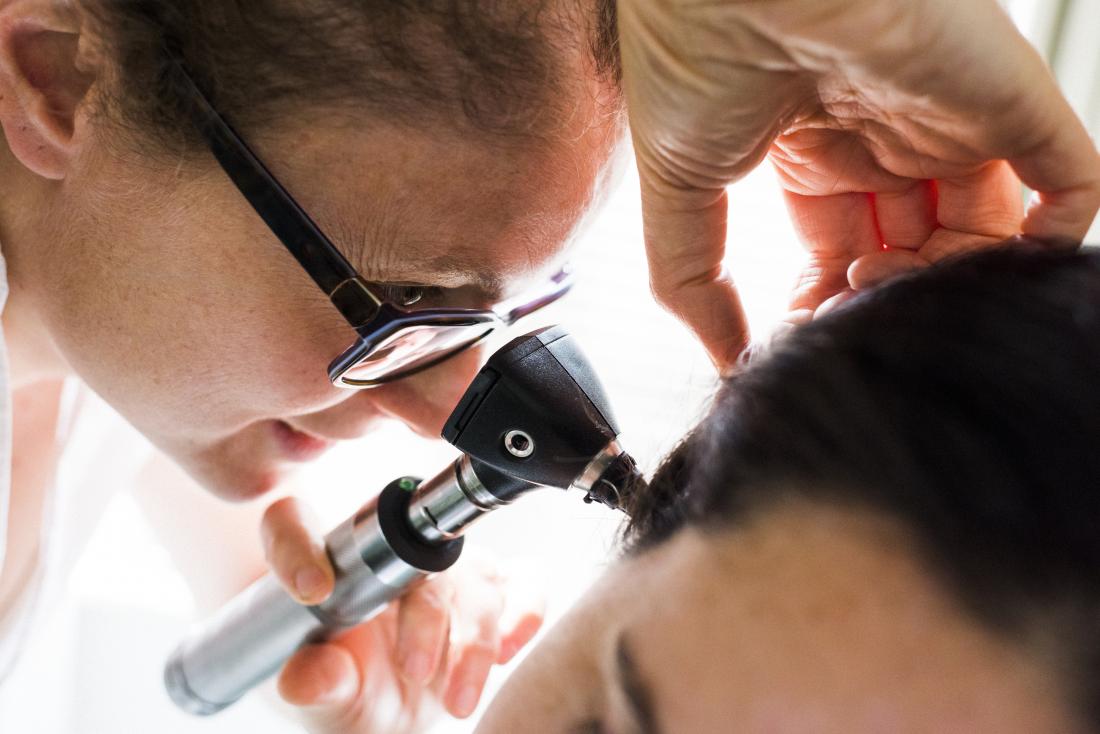
A doctor will use an otoscope during an ear examination.
A doctor will use an otoscope, which is a lighted microscope, to examine the ear and try to identify the underlying cause of the drainage.
They may also use a pneumatic otoscope that produces a puff of air to show how the eardrum moves in response to pressure. Doing this can show whether there is a buildup of fluid behind the eardrum.
A test called tympanometry can help doctors examine the health of the middle ear. To do this test, a doctor will insert a probe into the ear and evaluate how the middle ear responds to different pressure levels.
During an ear examination, doctors may also carry out a hearing test or use a tuning fork to test hearing levels.
Doctors will often prescribe antibiotics for some types of infection, which people can take either by mouth or as ear drops depending on the location of the infection in the ear.
To help ease earache, people can use a warm compress on their ear or take over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen.
A ruptured eardrum will often heal without treatment within a few weeks to 2 months. People can help the healing process and prevent infections by keeping their ear dry and protecting it from loud noises and physical knocks.
If an eardrum does not heal by itself, surgery may be necessary to patch new skin over the hole.
A doctor may prescribe antibiotics to treat ear fluid. The combination of a decongestant and an antihistamine can help reduce congestion.
If this treatment is not effective, the doctor can place an ear tube through the middle ear to allow fluids to drain as usual.
People can help prevent conditions that cause ear drainage by taking steps to care for their ears, such as:
- using earplugs in the ear when swimming to help keep water out and prevent infection
- blowing the nose gently, not forcefully
- carefully drying the outside of the ears after getting them wet
- avoiding inserting any objects into the ear

If a person has a fever along with ear drainage, they may wish to consult their doctor.
People should see their doctor if they experience any of the following:
- blood, clear fluid, or pus leaking from the ear
- ringing or loss of hearing in the ear
- symptoms of a ruptured eardrum that persist for longer than 2 months
- severe pain in the ear
- a high fever
- swelling and inflammation behind the ear
If people notice any drainage from the ear after a head injury, they should seek medical help immediately.
Ear drainage can include:
- earwax
- blood
- pus
- cloudy fluid
- clear fluid
Ear drainage can occur for several reasons, including an ear infection, a ruptured eardrum, or an ear tube that causes fluid to drain.
Ear discharge can sometimes be a sign of something more serious, especially if it occurs after a recent head injury. If people notice any ear drainage after a head injury, they should seek immediate medical help.
