While rheumatoid arthritis (RA) primarily affects the joints, it can cause inflammation to develop in other parts of the body, such as the lungs. This can make it difficult to breathe.
When the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells, it can cause inflammation in various parts of the body, including the joints and the lungs. When RA affects the lungs, it is known as rheumatoid lung disease.
Rheumatoid lung disease can cause breathing difficulties, so timely intervention is crucial for effective management.
In this article, we explore how rheumatoid arthritis affects the lungs. We also discuss its symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, outlook, complications, and when to seek medical attention.
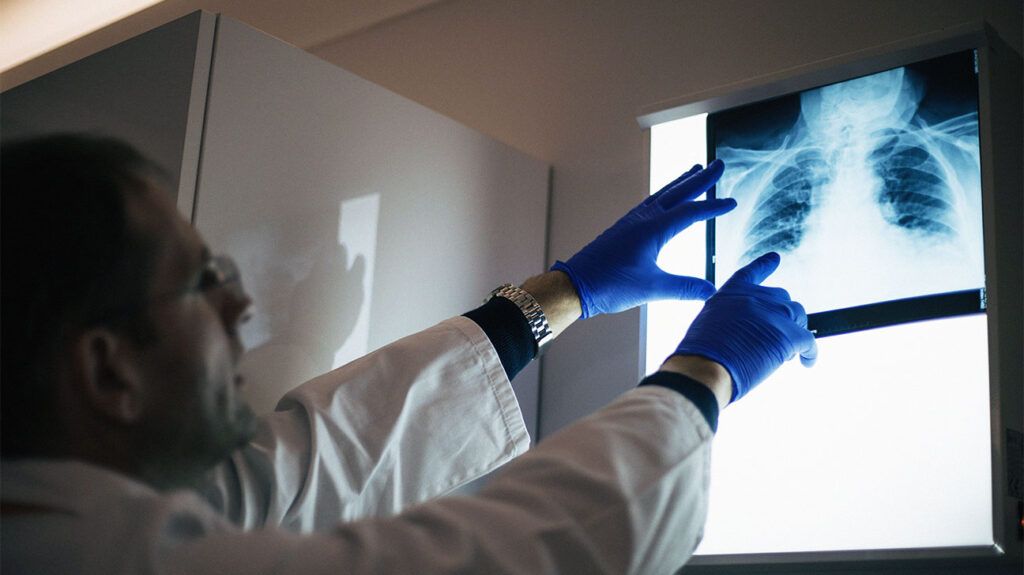
Aside from the joints, the lungs are the
Inflammation occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells in the body, causing painful swelling. When RA causes inflammation in the lungs, it is known as rheumatoid lung disease. Different types of this condition exist.
A common type of rheumatoid lung disease is interstitial lung disease (ILD), which refers to a group of diseases that cause scarring or stiffness in the lungs. Scarring of the lungs can affect how much oxygen gets into the bloodstream, which can affect a person’s breathing.
The symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis affecting the lungs can vary widely, depending on the underlying cause. Respiratory symptoms can
These symptoms may be more common during physical activity, and some people may also experience fatigue, weight loss, and a general feeling of discomfort.
Many of the symptoms of rheumatoid lung disease also occur with other respiratory conditions, so it is important to consult a doctor.
Generally, diagnosing rheumatoid lung disease requires a multidisciplinary approach involving healthcare professionals such as:
Healthcare professionals may conduct various tests to assess lung function and detect any issues. Tests may include:
- a physical exam
- pulmonary function tests
- chest X-rays
- high-resolution CT scans
- a bronchoscopy with biopsy
Treatment for rheumatoid lung disease will vary depending on a person’s symptoms, the specific lung condition, and how it affects their health.
Seeking early treatment for rheumatoid lung disease is essential.
While treatment cannot reverse any existing damage, it may help slow the progression of rheumatoid lung disease, which can help manage symptoms and improve lung function.
Options may include:
- Corticosteroids and immunosuppressants: These treatments reduce inflammation and suppress the immune system. Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs
can help relieve symptoms, maintain function, and prevent further damage to the joints. - Oxygen therapy: This treatment can provide extra oxygen to the lungs. A doctor may prescribe it alongside aerobic exercises to improve lung function.
- Lung transplant: In some cases, a lung transplant can be an effective and necessary option to regain lung function.
- Biologic therapies: These work by blocking the activity of a certain chemical, cell, or protein involved in inflammation. They are powerful therapies that target very specific parts of the immune system.
The outlook for people with rheumatoid lung disease varies depending on the severity of lung involvement, the type of lung disease, and treatment response.
Rheumatoid lung disease may sometimes be difficult to treat. It is a progressive disease, which means it can worsen over time, and it has a
Different factors may also affect survival rates — these include:
- the type of ILD a person has
- how long the person has had RA
- when a person receives an ILD diagnosis
- the extent of the disease
- whether lung tissue scarring is present
- being of an older age
- being male
- being a smoker
Generally, early diagnosis and appropriate management can improve outcomes and quality of life.
Without adequate management or treatment of rheumatoid lung disease, it can lead to severe complications such as:
- pulmonary fibrosis, which refers to a buildup of scar tissue in the lungs
- pulmonary hypertension
- a higher risk of respiratory infections
These complications can worsen breathing difficulties and significantly affect overall health and well-being. All of these can affect life expectancy.
People with rheumatoid arthritis who experience persistent respiratory symptoms should seek medical attention promptly. This includes experiencing the following:
- shortness of breath
- chest pain
- a chronic cough
A doctor can help determine the underlying cause.
In some cases, rheumatoid arthritis (RA) affects not only joints but also the lungs. The lungs are the most common part of the body where individuals with RA develop inflammation, aside from the joints.
When RA affects the lungs and causes symptoms, it is known as rheumatoid lung disease. The term refers collectively to lung conditions that RA causes. One type is Interstitial lung disease.
Inflammation occurs due to the immune system attacking healthy cells in the body by mistake, causing painful swelling.
Understanding the symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for rheumatoid lung diseases is crucial for improving outcomes and quality of life for those affected. Early detection and appropriate management are key to minimizing lung damage and optimizing overall health.
