A flexible bronchoscopy is a medical procedure that allows a doctor to examine the inside of the airways. Doctors pass a tube-like device into the airways to diagnose medical conditions, take biopsies, and perform minor treatments.
A flexible bronchoscopy involves using a long, thin, flexible tube with a light on the end to examine the inside of the airways.
A person may require a flexible bronchoscopy if a doctor suspects they have a respiratory condition, such as an infection, fluid in the lungs, or a blockage in the airways.
In this article, we will discuss what a flexible bronchoscopy is, when it may prove useful, which technique a doctor may use, how to prepare for the procedure, and any risks or complications involved.
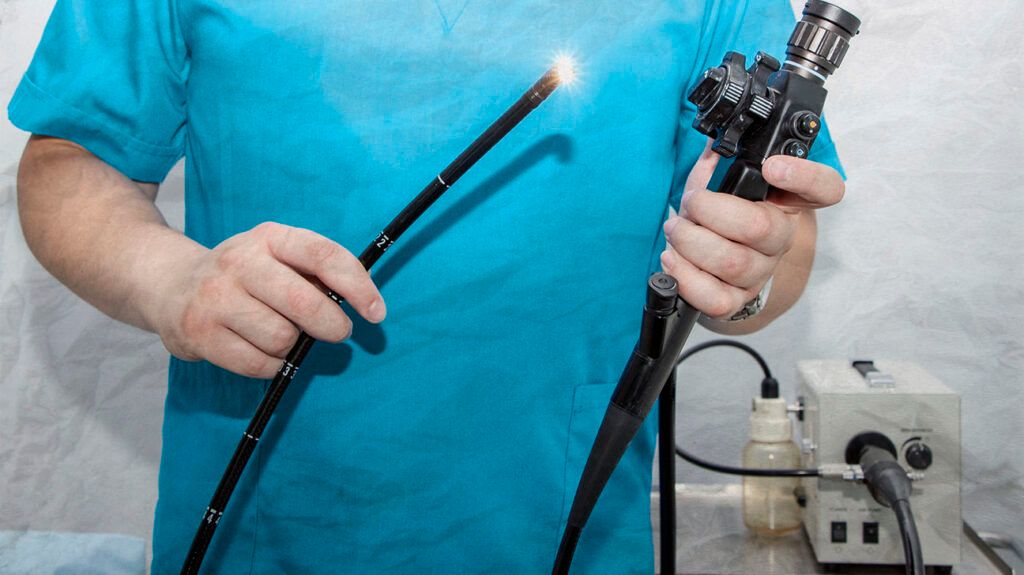
During the procedure, a doctor passes the bronchoscope into a person’s airways to
There may also be a small camera on the end of the bronchoscope, which allows a doctor to take images from inside the airways.
During a flexible bronchoscopy, a doctor may take small samples from inside the airways for further testing.
A doctor may also perform minor treatments such as draining an abscess or removing fluid from the airways during a flexible bronchoscopy.
Samples
During this procedure, a doctor may want to take biopsy samples — small pieces of tissue from the affected area — to help diagnose any respiratory conditions. Some of the procedures for sample collection
- passing a salt solution through the airways to collect cell samples from the lower respiratory tract and lungs
- bronchial brushing, which involves passing a tiny brush into the airways to collect cell samples
- passing a small needle through the bronchoscope to collect tissue samples from the lungs and lymph nodes
- passing small forceps through the bronchoscope to collect cell and tissue samples from the lungs and lymph nodes
A flexible bronchoscopy may prove useful if a doctor suspects a person has any abnormalities in the airways and lungs and wants to gain a clearer picture.
The procedure can also be useful if a doctor wants to take biopsy samples from the lungs and airways for testing.
During a flexible bronchoscopy, a doctor can perform minor treatments,
- removing any blockages and cleaning out the airways
- draining an abscess
- removing fluid from the lungs
- widening any narrowing airways
To begin a flexible bronchoscopy, a person will lie on their back and may require sedation medication or local anesthesia to make the procedure more comfortable. Sedation medication can relax a person, and local anesthetics can numb the back of the throat.
A doctor will then pass the flexible bronchoscope through the throat or nose, into the windpipe, and down into the lungs. The doctor can then examine the airways, take biopsy samples, capture images, and perform any necessary procedures.
At the end of the procedure, the doctor will slowly draw out the bronchoscope. The whole procedure may take approximately 45–60 minutes.
To prepare for flexible bronchoscopy, a person may have to refrain from eating or drinking anything for approximately 8 hours before the procedure.
A person should avoid smoking for 24 hours before the procedure.
A doctor may need to take blood tests and may ask a person to avoid certain medications, such as blood thinners, in the lead-up to the procedure.
During flexible bronchoscopy, a person may feel discomfort, such as gagging and breathlessness. A person will not be able to talk during the procedure.
Following flexible bronchoscopy, a person may experience a sore throat, hoarse voice, small amounts of blood when coughing, and a fever for up to 24 hours.
A person should avoid eating or drinking until the local anesthetic wears off, which may take approximately 1 hour.
A flexible bronchoscopy is typically a safe procedure. However, there are several complications that may occur, including:
- bleeding, particularly if a doctor takes a biopsy sample
- collapsed lung, which is a rare complication
- infection in the lungs or airways
- reaction to the anesthetic, such as nerve damage or seizure
Common questions about flexible bronchoscopy include:
What is flexible bronchoscopy used for?
A doctor
What is the most common indication for flexible bronchoscopy?
The most common indications for flexible bronchoscopy are airway blockage or inability to clear liquid from the lungs.
What are the risks of flexible bronchoscopy?
Risks of flexible bronchoscopy can include bleeding, sore throat, hoarse voice, fever, infection, and collapsed lung.
How long does a flexible bronchoscopy take?
A flexible bronchoscopy typically takes between 45 and 60 minutes.
A flexible bronchoscopy is a medical procedure involving a bronchoscope. This device is a long, flexible tube with a light and camera on the end. The procedure allows a doctor to examine the inside of the lungs and airways to identify any abnormalities.
A doctor can also take biopsy samples and perform minor treatments during a flexible bronchoscopy.
Before a flexible bronchoscopy, a doctor may recommend fasting, avoiding smoking, and temporarily stopping medications.
The procedure may take between 45 and 60 minutes and may involve some risks, including bleeding, infections, and collapsed lung. However, flexible bronchoscopy is typically safe.
